Deploy an AI model
With Gcore Everywhere Inference, you can use foundational open-source models from our AI model catalog or deploy a custom model by uploading a Docker container image.
Info
You might have to request a quota increase before deploying a new model; the Request quota increase guide explains this process.
Step 1. Initialize a new deployment
This step will differ slightly depending on whether you deploy a custom model or use a model from our catalog.
Tip
Before you continue, refer to the Prepare a custom model for deployment guide if you want to deploy a custom model to Everywhere Inference.
You can initialize a new deployment by opening this direct link to the deployment form or by following these three simple steps:
1. In the Gcore Customer Portal, navigate to Everywhere Inference > Deployments.
2. Click the Deploy model from catalog button in the top right of the screen.
3. Select the desired model from the Model dropdown.
You can initialize a new deployment by opening this direct link to the deployment form or by following these three simple steps:
1. In the Gcore Customer Portal, navigate to Everywhere Inference > Deployments.

2. Click the Deploy model from catalog button in the top right of the screen.

3. Select the desired model from the Model dropdown.

You can initialize a new deployment by opening this direct link to the deployment form or by following these steps:
1. In the Gcore Customer Portal, navigate to Everywhere Inference > Deployments.
2. Click the Deploy custom model button in the top right of the screen.
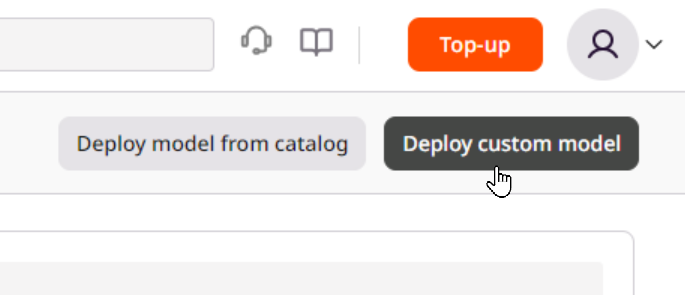
3. If you choose to deploy a model from a public registry, enter the image URL, Docker tag, and container port where the model will listen for requests.
Optionally, you can enable the Set startup command toggle to define a command executed when the container starts.
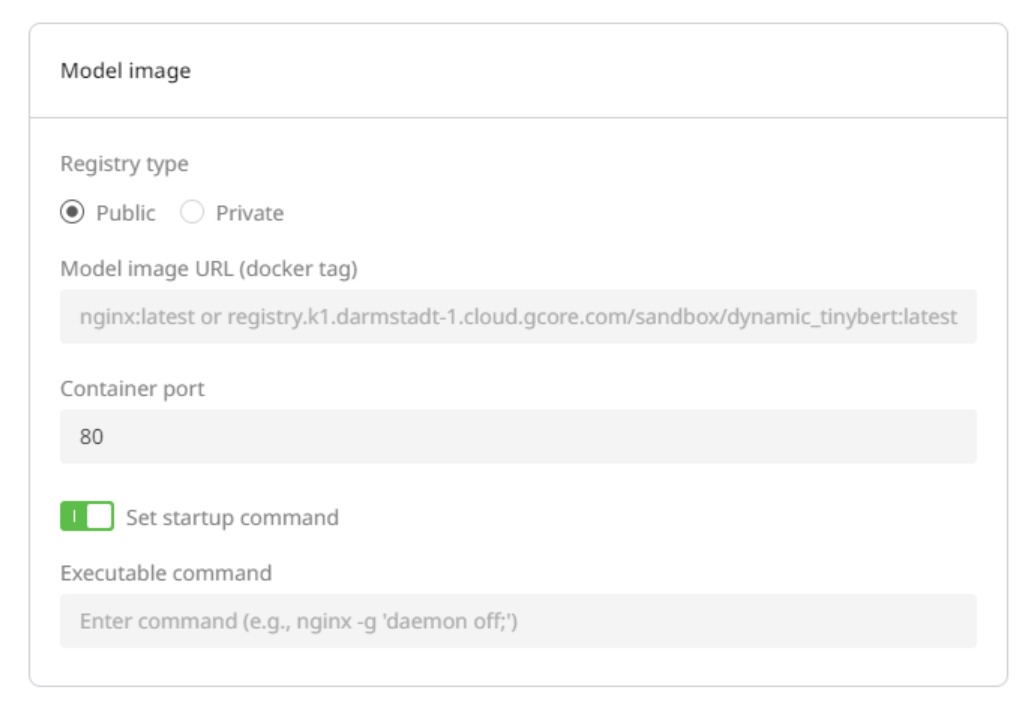
If you want to deploy a model from a private registry, select the Private Registry type, enter the image URL, Docker tag, and the container port where the model will listen.
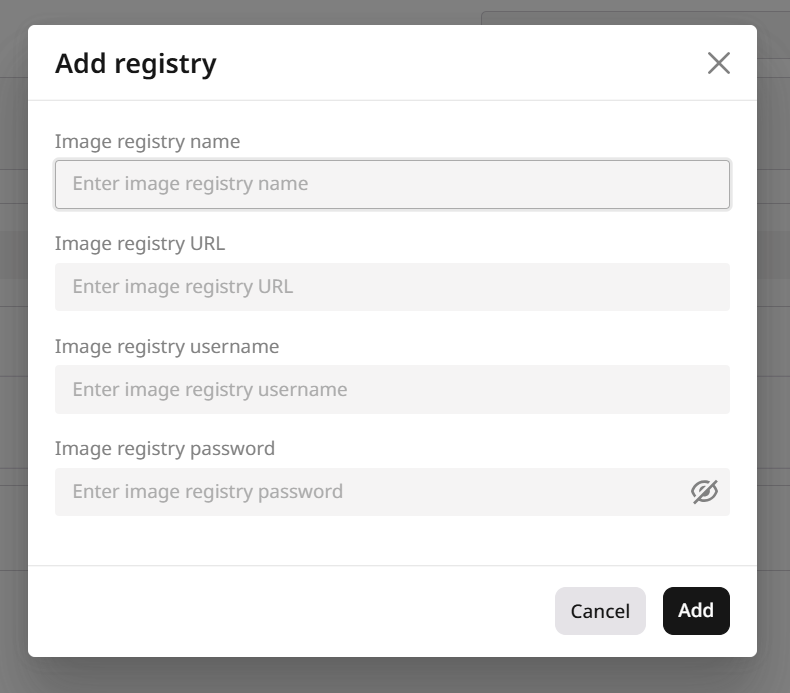
If you haven’t added a registry to Everywhere Inference yet, click Add registry. This will open a dialog where you can define your private registry URL and login credentials. Check out the registry guide to learn more about creating and managing your registries.
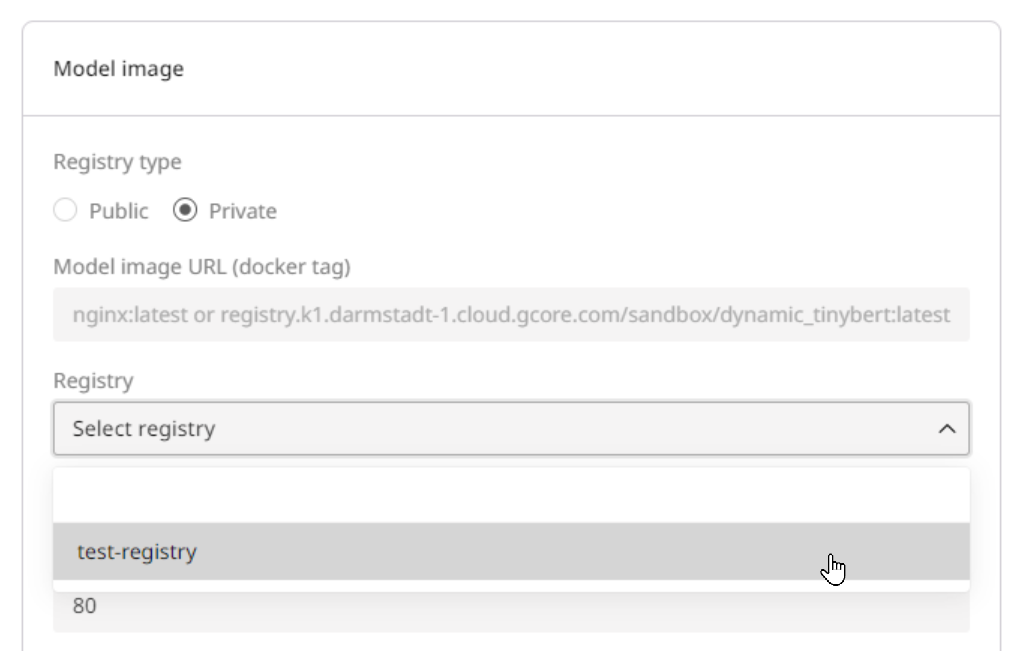
Select the relevant registry from the Registry dropdown.
Step 2. Select a pod configuration
This configuration determines the allocated resources (e.g., GPU, vCPU, and memory) for running the model. Be sure to select sufficient resources; otherwise, the model deployment might fail.
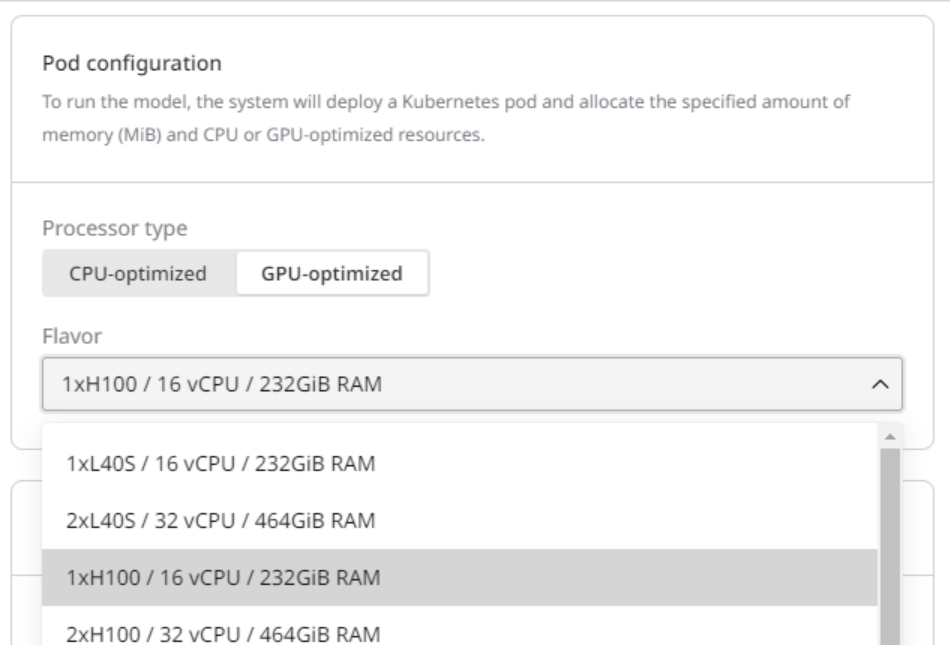
We recommended the following flavor parameters for models:
| Billion parameters | Recommended flavor |
|---|---|
| < 21 | 1 x L40s 48 GB |
| 21 - 41 | 2 x L40s 48 GB |
41 | 4 x L40s 48 GB
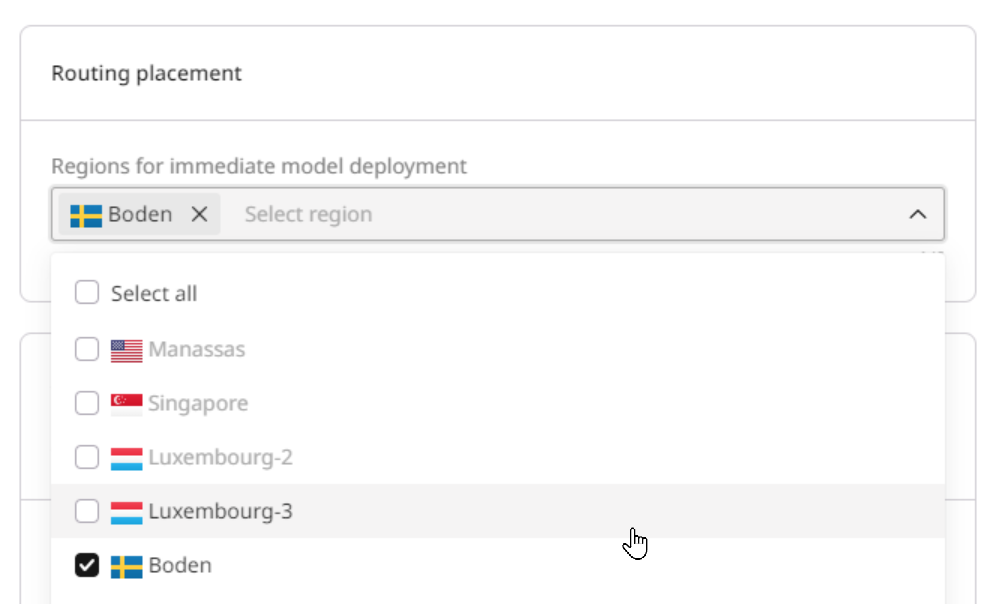
Step 3. Set up routing placement
Select the inference regions where the model will run from the worldwide points of presence (PoPs) list. The list of available PoPs depends on which pod configuration you selected in Step 3.
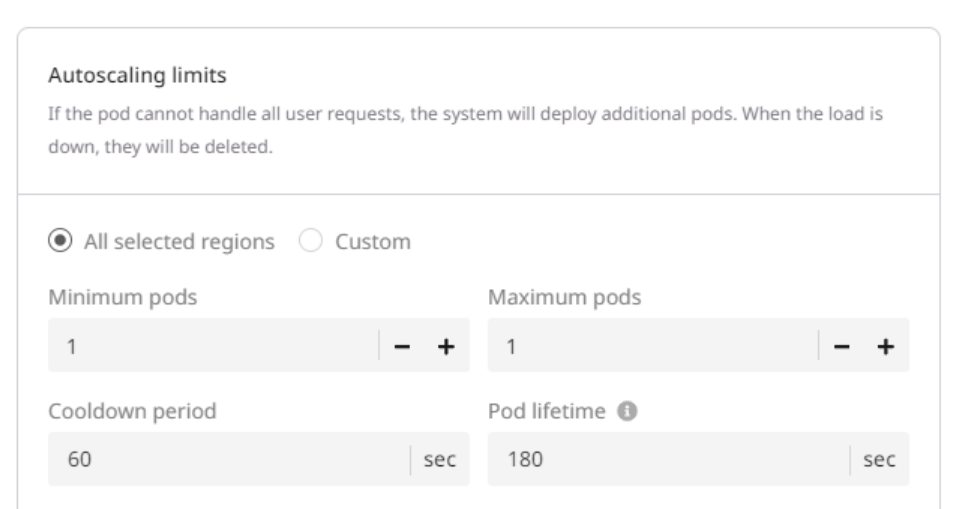
Step 4. Configure autoscaling
You can set up autoscaling for all pods (All selected regions) or only for pods located in specific areas (Custom).
1. Specify the range of nodes you want to maintain:
- Minimum pods: The minimum number of pods must be deployed during low-load periods.
- Maximum pods: The maximum number of pods that can be added during peak-load periods.
- Cooldown period: A configured time interval that the autoscaler waits after scaling an application (up or down) before it considers making another scaling adjustment
- Pod lifetime: The time in seconds that autoscaling waits before deleting a pod that isn’t receiving any requests. The countdown starts from the most recent request.
Info
A pod with a lifetime of zero seconds will take approximately one minute to scale down.
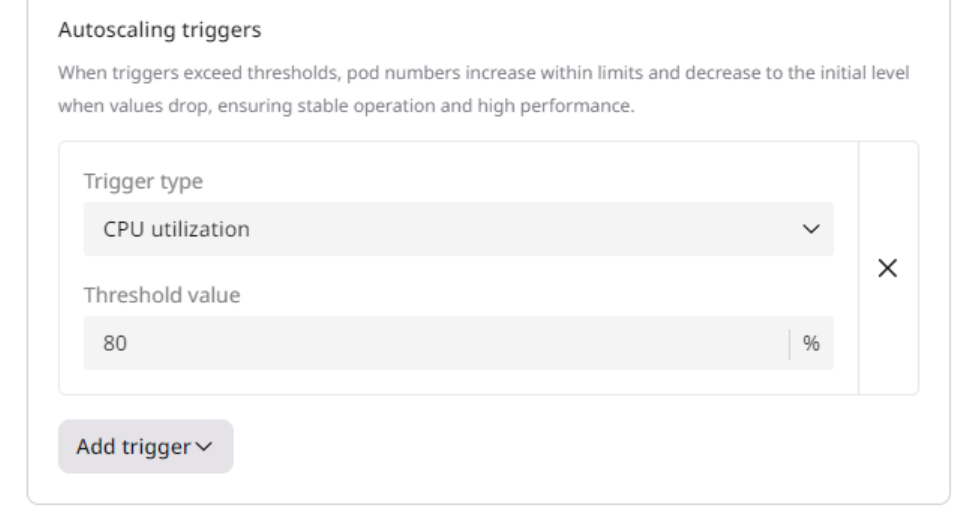
2. Define the events that should trigger the provisioning of a new pod:
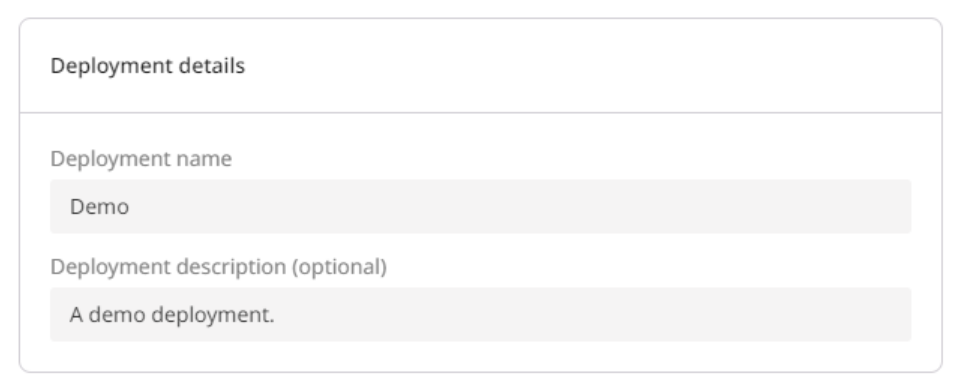
Step 5. Set deployment details
Your deployment needs a name to make it easy to identify later. You can optionally add a description.
Step 6 (optional). Set environment variables and API Keys
If you want to add additional information to the deployment, create variables for your container in key-value pairs. These variables will only be used in the environment of the created container. To access the environment variables settings, turn on the Set environment variables toggle.
You can also configure API authentication for your deployment. To access the authentication settings, turn on the Enable API Key authentication toggle.
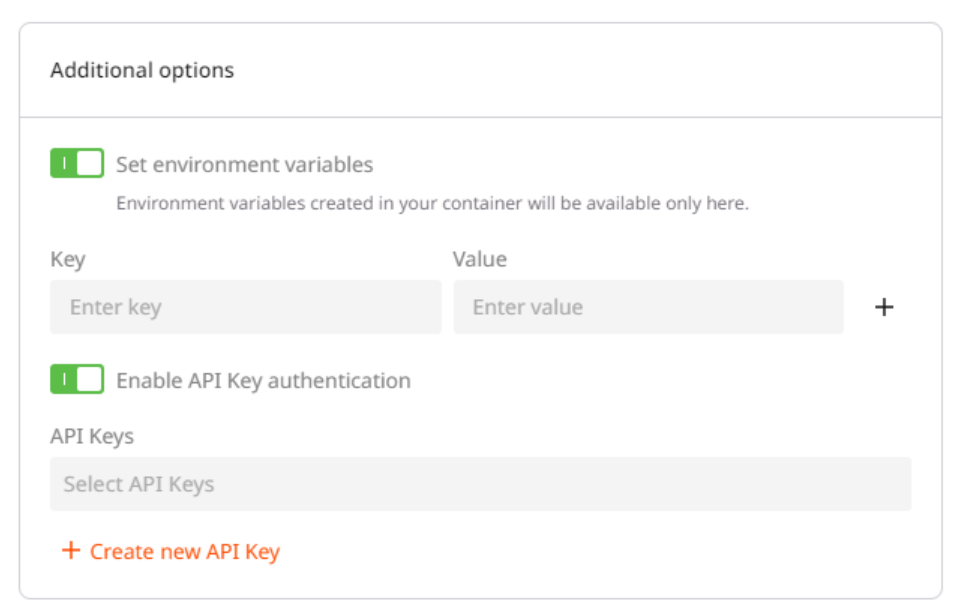
Tip : Multiple API keys can be associated with a single deployment, and the same API key can be attached to multiple deployments.
If you haven’t created an API key yet or want to use a new key for this deployment, click on Create a new API Key.
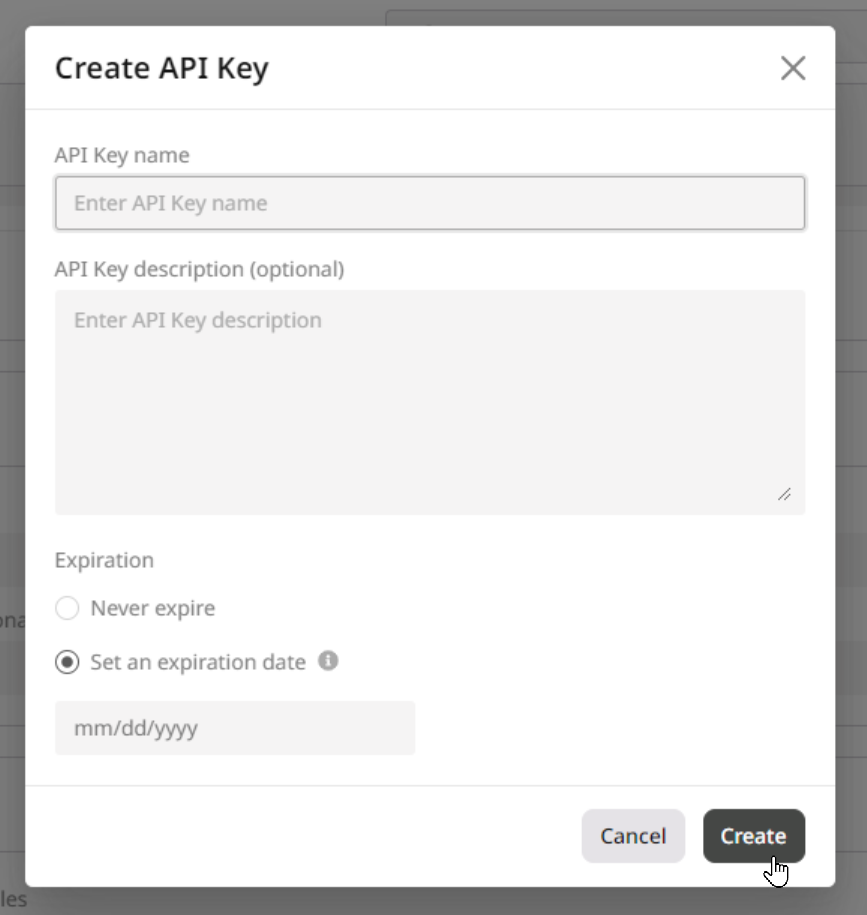
1. In a new dialog that opens, enter the key name to identify the key in the system. 2. (Optional) Add a key description to give more context about the key and its usage. 3. As a security measure, you can specify the key expiration date. If you don’t want to regenerate the key and instead want to keep it indefinitely, choose Never expire. 4. Click Create to generate the key.
After you generate the key, it will appear in the API Keys dropdown. You can then select it to authenticate to the deployment. Check out the API Keys guide for instructions on authenticating with the API key.
Step 7. Finalize the deployment
Scroll to the top of the page and click Deploy model in the top-right corner of the screen.
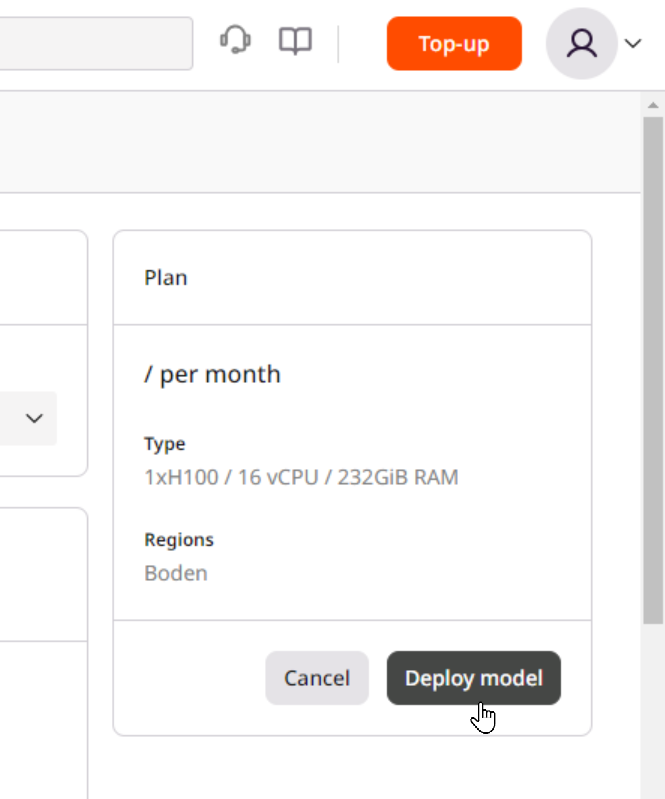
Info
If you don’t see the Deploy model button, add billing information to your account or create a quota change request.

